Medical devices
Containers for blood collection, storage and preparation
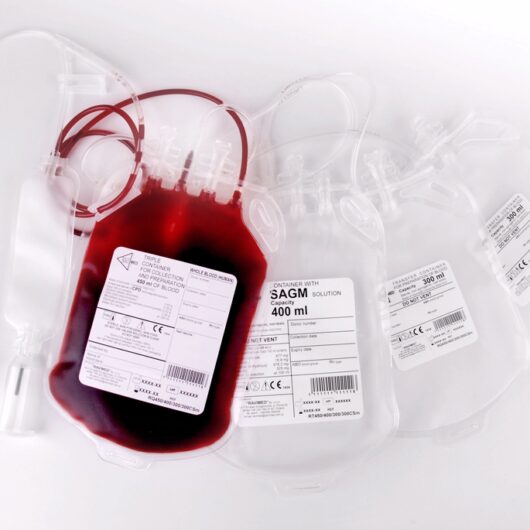
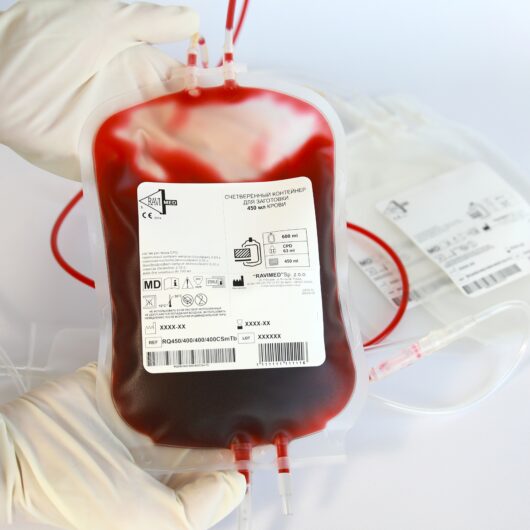
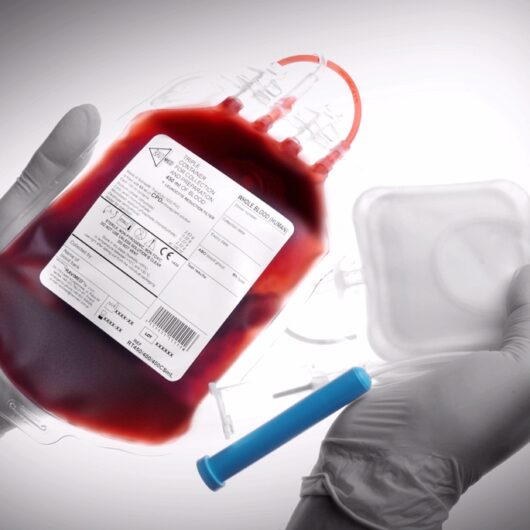
Since 1991, Ravimed has been manufacturing a Set of containers used in the collection, storage and processing of blood which represent a closed system for the optimal use of blood and blood components.
The preservatives (anticoagulants) and the blood enrichment liquids may contain citric acid, sodium citrate, sodium phosphate, glucose, adenine, sodium chloride and mannitol:
- ACD-A – Acid citric, Citrate, Dextrose (glucose);
- CPDA-1 – Citrate, Phosphate, Dextrose, Adenine,
- CPD – Citrate, Phosphate, Dextrose,
- SAGM – Saline (Sodium chloride), Adenine, Glucose, Mannitol;
and provide anticoagulation of whole blood and its storage for:
- CPD – 21 days
- CPDA-1 – 35 days
- SAGM – 42 days
1. top-top
- single
- drawing and storage of whole blood;
- double
- splitting whole blood into two parts
- separation of red blood cells from plasma
- triple
- splitting whole blood into three parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, platelets and plasma
- quadruple
- splitting whole blood into four parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and plasma;
- fivefold
- splitting whole blood into four parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and plasma;
- sixfold
- splitting whole blood into four parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and plasma;
- double plasmapheresis
- for plasma acquisition by separating red blood cells from plasma and returning them to the donor.
2. top-down (developed and implemented thanks to European Union funds)
- triple
- splitting whole blood into three parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, platelets and plasma
- quadruple
- splitting whole blood into four parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and plasma;
- fivefold
- splitting whole blood into four parts
- blood separation into red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets and plasma;
- ”A” for drawing cord blood
- for cord blood preparation to obtain the maternal blood cell preparation
Blood preparation fluids
Warning: Invalid argument supplied for foreach() in /raviwww2/wp-content/themes/ravimed/templates/oferta.php on line 34
Intended use of blood preparation fluids:
- Blood preparation fluids (ACD-A, 4% sodium citrate in 0.9% NaCl solution)
- Cryoprotective fluids
- freezing (cryopreservation) by glycerol technique
- defreezing with simultaneous deglycerolisation of red blood cells
- Laboratory blood preparation solution (HES)
- reduction in cord blood volume by erythrocyte sedimentation


